Public confidence in health authorities providing trustworthy information about the means of preventing and treating Covid-19. From a survey conducted with a nationally representative sample of 1,621 U.S. adults November 3-9, 2021, by the Annenberg Public Policy Center of the University of Pennsylvania. Courtesy of Annenberg Public Policy Center
Twenty-one months into the global pandemic, millions of Americans continue to believe misinformation about vaccination and Covid-19, and these beliefs are associated with hesitancy to get themselves and their children vaccinated – or, if they are vaccinated, to get a booster for added protection against the omicron and delta variants.
In the fourth survey conducted with a nationally representative sample of more than 1,600 U.S. adults, in November 2021 the Annenberg Public Policy Center of the University of Pennsylvania continued its tracking of misbeliefs and conspiracy theories that have persisted and, in rare cases, grown since the inception of the pandemic. The policy center has been conducting this panel study since April 2021, and began tracking beliefs about the novel coronavirus and vaccination even earlier, with cross-sectional surveys beginning in March 2020.
“Key consequential deceptions continue to predict hesitancy for oneself and one’s children and a reluctance to get a booster,” said Kathleen Hall Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC). “Even though more people reject these conspiracies and misbeliefs than accept them, those that have become deeply rooted need to be repeatedly fact-checked, highlighted, and countered by media organizations and health care providers.”
Although confidence in him remains high, the survey also found a softening of support for Dr. Anthony Fauci, who directs the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). With two-thirds of Americans confident Fauci is providing trustworthy information on treating and preventing Covid-19, the group of those who support him most strongly has diminished while the ranks of those with no confidence have grown.
Highlights: Misinformation
The Annenberg Public Policy Center’s Annenberg Science Knowledge (ASK) survey shows that beliefs in conspiracies and misinformation have changed over time. All of the changes noted here between different waves of this survey are statistically significant:
- Nearly a third of those surveyed in November (31%) believe the conspiracy theory that the Chinese government created the coronavirus as a biological weapon – more than in March 2020 (23%), days before the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a pandemic;
- While a growing majority (79%, up from 71% in April 2021) rejects as false the conspiracy theory that Microsoft cofounder Bill Gates supported development of a vaccine containing microchips that can track a vaccinated person, 1 in 5 people (21%) still think it is true (8%) or are not sure (13%).
- Over half of those surveyed (56%) correctly know that the Moderna and the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines do not contain fetal tissue, up from 51% in April 2021. But a growing minority (15%, up from 11% in September and 9% in April) say that this is true and about a third (30%) are not sure whether it is true or false.
The November Annenberg Science Knowledge (ASK) survey is the fourth wave of data from a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults empaneled by the policy center in the spring of 2021. The survey was conducted November 3-9, 2021, among a national probability sample of 1,672 U.S. adults. Data were weighted to represent the target U.S. adult population. The margin of error for the total sample is ± 3.3 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. The panel survey, conducted for the Annenberg Public Policy Center by SSRS, an independent research company, is a follow-up to September 2021, June 2021 and April 2021 surveys fielded with the same respondents. See the Appendix for the methodology, question wording, and additional data.
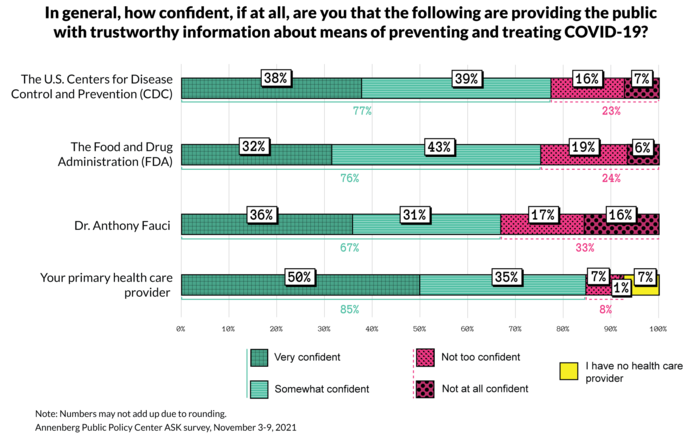
Trust in health authorities
An individual’s primary healthcare provider continues to be the most trusted source of information about the means of preventing and treating Covid-19. The survey found no statistically meaningful changes in overall confidence from September to November:
- Primary healthcare provider: 85% are confident their primary health care provider is providing trustworthy information about Covid-19;
- Food and Drug Administration: 76% are confident that the FDA, which authorized emergency use of Covid-19 vaccines in the U.S. and gave full approval to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine for adults in August, is providing trustworthy information on Covid-19;
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: 77% are confident the CDC is providing trustworthy information on Covid-19;
- Dr. Anthony Fauci: 67% are confident that Fauci, director of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious
Although Americans’ overall confidence in Fauci is statistically unchanged since pollsters first asked this question in August 2020, the data suggest that confidence has weakened. The survey finds a diminishing percentage of those with the highest degree of confidence (36%, down from 41% in April) and a growing percentage of those with no confidence (16%, up from 12% in April). Overall confidence remains unchanged because the shift exists among those who are “very confident” moving to “somewhat confident,” and among those who shifted from “not too confident” to “not at all confident.”
While a plurality of people previously said Fauci has no financial stake in any Covid-19 vaccine, opinion on that question is now evenly divided. The survey finds a 37%-37% split on whether it is true or false to say that Fauci has no financial stake in any vaccine compared with April 2021, when by a 42% to 28% margin more said he did not have a financial stake. Fact-checkers have debunked narrower claims about Fauci’s alleged ties to Pfizer and Moderna. National Institutes of Health scientists are on patents related to the Moderna vaccine but Fauci is not one of them.
Lower confidence among conservative media users
As the earlier waves of the survey have also found, heavier users of conservative and very conservative media have significantly less confidence in U.S. health authorities, notably Fauci, the CDC, and the FDA.
Among the heavier users of:
- Very conservative sources such as Newsmax, One America News (OAN), Gateway Pundit, Parler, or Telegram: 46% have confidence in Fauci, 50% in the CDC, 54% in the FDA, and 86% in their primary health care provider;
- Conservative media such as Fox News, Mark Levin, or Breitbart: 47% have confidence in Fauci, 59% in the CDC, 64% in the FDA, and 90% in their primary health care provider;
- Social media such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, or YouTube: 71% express confidence in Fauci, 76% in the CDC, 72% in the FDA, and 86% in their primary healthcare provider (down significantly from 94% in September);
- Mainstream broadcast/print media such as CBS News, NBC News, ABC News, the Associated Press, or the news pages of The Wall Street Journal or The New York Times: 87% express confidence in Fauci, 91% in the CDC, 90% in the FDA, and 95% in their primary healthcare providers.
In this survey, heavier users of social media did not have significantly lower confidence in health authorities than the overall sample. Except as noted above, there were no statistically meaningful changes among these measures from September to November.
Conspiracy theories
The November survey tracked public responses on these conspiracy theories:
- The Chinese bioweapon theory: Over half of those surveyed (53%) either thought it is true (31%) that the Chinese government created the coronavirus as a biological weapon or were not sure (22%). The proportion of those who said it is true increased by eight points since March 2020 (23%).
- The Bill Gates-microchip theory: Nearly 4 out of 5 people (79%) correctly say it is false that “the vaccine against Covid-19 being developed with support by Microsoft founder Bill Gates contains microchips that can track the person who has been vaccinated.” But more than 1 in 5 people are either not sure (13%) or consider this true (8%).
- The CDC and exaggerated danger: Over a quarter of those surveyed (27%) continue to hold the belief that some health officials at the CDC exaggerated the danger posed by the pandemic to damage the Trump presidency. Another 14% are not sure if this is true and 58% say it is false. This has not changed since April 2021.
- The 5G wireless technology theory: Only a small group (5%) say that social distancing orders are secretly meant to allow the installation of 5G wireless technology, while 15% say they are not sure and 80% say it is false.
- Vaccines and the Black and Hispanic communities: A small group (6%) say that the Covid-19 vaccines were designed to control the size of the Black and Hispanic communities, while 13% are not sure and 81% say this is false.
Vaccine information and misinformation
The survey also examined beliefs in other types of information and misinformation, some of which are consistent with findings in a recent Kaiser Family Foundation survey. Ken Winneg, PhD, APPC’s managing director of survey research, ran a series of regressions to measure the association between beliefs in misinformation and conspiracy theories and the likelihood of vaccination. In the presence of statistical controls, he found a significant association between individuals’ belief in misinformation and conspiracy theories and vaccine hesitancy for themselves and their children, and reduced likelihood that the individuals would report getting a booster, if they are already vaccinated.
Other survey findings include (all the changes over time noted here are statistically significant):
- Vaccine safety: Nearly 4 in 5 people (79%) said it is probably or definitely true that the vaccines approved for use in the United States are safe. Of this group, 43% said it is definitely true, up from June (38%) and April (34%). Just 10% said it is false.
- Vaccine effectiveness: Nearly 3 in 4 people (73%) say the Covid-19 vaccines are effective in preventing Covid-19, unchanged since September. The question was asked in early November, prior to awareness of the omicron variant.
- Fetal tissue: Most of those surveyed correctly say it is false to say that the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines contain fetal tissue (56%, up from 51% in April). A small but growing minority says it is true (15%, up from 9% in April) and 30% of those surveyed are not sure.
- DNA: Three-quarters of those surveyed (74%) correctly say it is false to state that Covid-19 vaccines change people’s DNA, more than in April (69%). One in 10 people (10%) says this is true and 17% are unsure, findings consistent with the Kaiser poll.
- Toxins: Three-quarters (77%) say it is false that childhood vaccines contain toxins such as antifreeze. Antifreeze is not used in vaccines, and vaccines with a variety of ingredients are tested for safety and effectiveness before they are licensed. T
- Infertility: Two-thirds (66%) say it is probably or definitely false to state that Covid-19 vaccines cause infertility and a growing number of those people say it is definitely false (41%, up from 36% in June). Just 1 in 10 (10%) say this is true, a finding similar to the Kaiser poll.
- Ivermectin: 18% of those surveyed say it’s true that ivermectin is an effective treatment for Covid-19 (up from 10% in September), while 38% think that is false (up from 27% in September).
Source: Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC)