Healthcare workers are at higher risk of hepatitis B infection due to occupational exposure to blood and body fluids. They are considered protected if they have a hepatitis B surface antigen antibody (anti-HBs) titer of ≥10 mIU/mL after completing a full vaccination series. This study by Williams, et al. (2025) in Annals of Family Medicine compared the effectiveness of Heplisav-B, a new hepatitis vaccine, vs. standard hepatitis B vaccines as a booster in previously vaccinated individuals.
Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, analyzing medical records from 2019 to 2022. The study included medical students who had completed a full hepatitis B vaccine series but had low antibody levels. Participants received either a standard hepatitis B booster or a Heplisav-B booster. Their antibody levels were measured at least 30 days later to determine if they had achieved protective immunity.
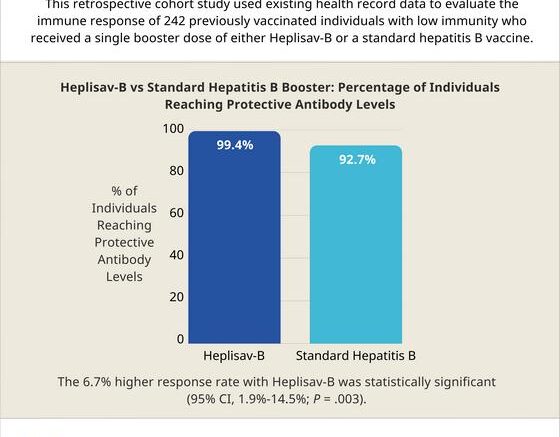
99.4% of individuals receiving Heplisav-B reached protective antibody levels. 92.7% of individuals receiving a standard booster reached protective levels. The 6.7% higher response rate with Heplisav-B was statistically significant (95% CI, 1.9%-14.5%; P = .003). All seven individuals who remained below protective levels after one booster reached immunity after receiving additional vaccinations.
The study findings suggest that a single booster dose is sufficient to confirm hepatitis B immunity in most young, healthy health care workers who previously completed a full vaccination series. Heplisav-B was more effective than standard hepatitis B vaccines.
Source: American Academy of Family Physicians