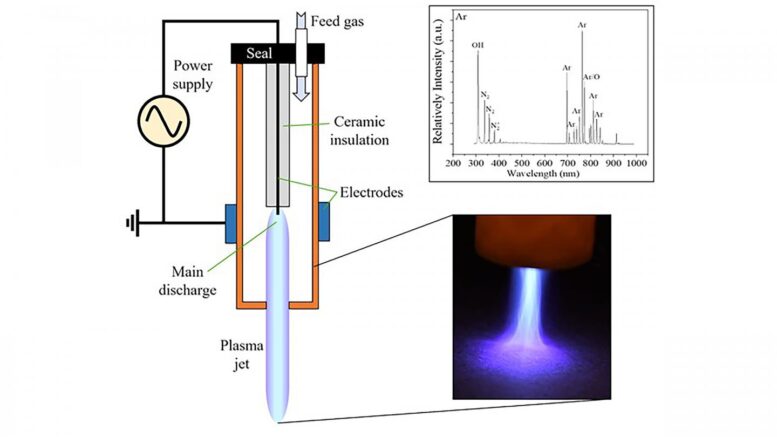
A schematic of UCLA's cold atmospheric plasma device with an image of it in operation. Courtesy of Wirz Research Group, UCLA
In a study published in Physics of Fluids, modeling conducted in June showed strains of the novel coronavirus on surfaces like metal, leather, and plastic were killed in as little as 30 seconds of treatment with argon-fed, cold atmospheric plasma.
The researchers used an atmospheric pressure plasma jet they built with a 3D printer to spray surfaces that were treated with SARS-CoV-2 cultures. The surfaces included plastic, metal, cardboard, and basketball, football, and baseball leather.
The spray using plasma fed by argon killed all the coronavirus on the six surfaces in less than three minutes, and most of the virus was destroyed after 30 seconds. Additional testing showed the virus was destroyed in similar times on cotton from face masks.
The novel coronavirus can remain infectious on surfaces for several hours. Author Richard E. Wirz said the findings show great potential for the use of plasma in halting the virus's transmission cycle.
"This is only the beginning," Wirz said. "We are very confident and have very high expectations for plasma in future work. In the future, a lot of answers for the scientific community will come from plasma."
Plasma is one of the four basic states of matter and can be created by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field. A relatively new technology, cold atmospheric plasma is an ionized, near-room-temperature gas that has proven effective in cancer treatments, wound healing, dentistry, and other medical applications.
The authors ran a similar coronavirus test with helium-fed plasma, but the helium was not effective, even with treatments up to five minutes. The authors believe this was due to lower rates of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen when using helium-fed gas, compared to argon.
Zhitong Chen said the authors are building a compact device that could be used widely to treat surfaces for the coronavirus with plasma. It is a safer, healthier option than chemicals or other treatments, he said.
"Everything we use comes from the air," he said. "Air and electricity: It's a very healthy treatment with no side effects."
The researchers hope the benefits of plasma, like those shown in this study, can be made available to people around the world.
The article, "Cold atmospheric plasma for SARS-CoV-2 inactivation," is authored by Zhitong Chen, Gustavo Garcia, Vaithilingaraja Arumugaswami, and Richard Edward Wirz. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on Nov. 10, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0031332 at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0031332.
Source: American Institute of Physics
Be the first to comment on "Plasma Treatments Quickly Kill Coronavirus on Surfaces"