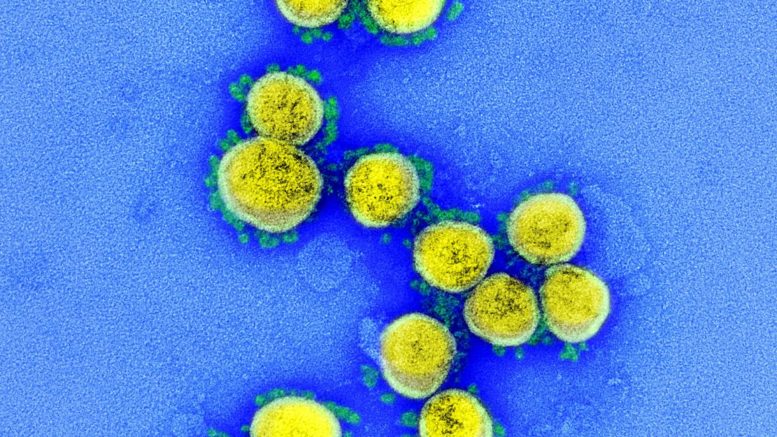
Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Md. Courtesy of NIAID
The National Library of Medicine (NLM), part of the National Institutes of Health, is working on multiple fronts to aid in the COVID-19 response through new initiatives with the global publishing community and artificial intelligence researchers. NLM is expanding access to scientific papers on coronavirus for researchers, care providers, and the public, and for text-mining research. This work makes use of NLM’s PubMed Central® (PMC), a digital archive of peer-reviewed biomedical and life sciences literature. PMC currently provides access to nearly 6 million full-text journal articles.
Following on a statement issued by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) and science policy leaders from almost a dozen other nations, NLM has stepped up its collaboration with publishers and scholarly societies to increase the number of coronavirus-related journal articles in PMC, along with available data supporting them. Submitted publications will be made available in PMC as quickly as possible after publication, in formats and with needed permissions to support text mining.
To support this initiative, NLM is adapting its standard procedures for depositing articles into PMC to provide greater flexibility that will ensure coronavirus research is readily available. NLM is also engaging with journals and publishers that do not currently participate in PMC but are in-scope for the NLM Collection. Interested publishers should contact pmc-phe@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov for information on participating in this initiative. Additional information, including a list of participating publishers and journals, is available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/about/covid-19.
By making this collection of coronavirus articles more readily available in machine-readable formats, NLM aims to enable artificial intelligence researchers to develop and apply novel approaches to text mining to help answer questions about coronavirus. NLM has already made more than 10,000 full-text scholarly articles from PMC related to the coronavirus available through the COVID-19 Open Research Dataset (CORD-19). The CORD-19 dataset, the result of a request by OSTP, represents the most extensive machine-readable coronavirus literature collection available for text mining to date.
NLM will continue to aid COVID-19 response efforts by adding articles to its text-mining collection as they are published and submitted. It will also aim to bring this collection to the attention of the artificial intelligence and machine learning research communities.
Source: National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Be the first to comment on "National Library of Medicine Expands Access to Coronavirus Literature Through PubMed Central"