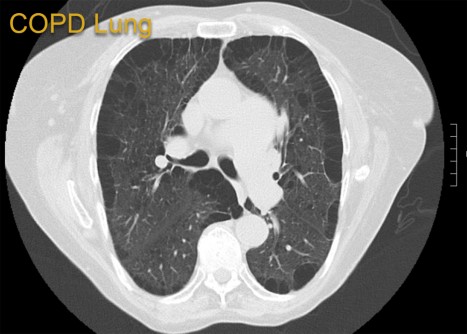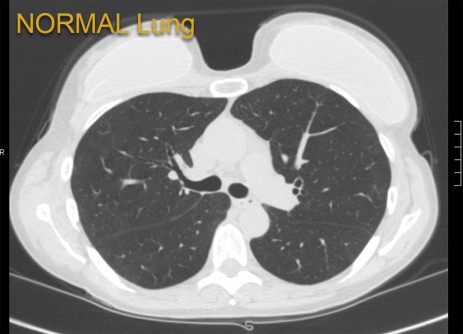
Normal lung. Courtesy of University of Maryland School of Medicine
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) analyzed data at the 13-hospital University of Maryland Medical System (UMMS) and found public health measures designed to reduce the spread of the COVID-19 virus may have fostered a substantial side benefit: Hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were reduced by 53 percent, according to a new study accepted for publication by a peer-reviewed medical journal and currently available at the online journal medRxiv. This is likely due to a drop in circulating seasonal respiratory viruses such as influenza.
Hospitalizations for COPD, a group of lung diseases that make it hard to breathe and get worse over time, are commonly driven by flare-ups where symptoms are triggered by such factors as tobacco smoke, air pollution and respiratory infections. Seasonal respiratory viruses, including those that cause the common cold or influenza, trigger nearly half of those flare-ups.
In the wake of a marked drop in COPD admissions during the pandemic, the researchers theorized that COVID-19 behavior changes – a mix of stay-at-home orders, social distancing, masking mandates and strict limitations on large gatherings – not only protected against COVID-19, but they may have also reduced exposure to other respiratory infections.
Conversely, they worry that the return to normal behavior may lead to more COPD flare-ups.
“Our study shows there’s a silver lining to the behavior changes beyond protecting against COVID-19,” said senior author Robert M. Reed, MD, UMSOM professor of medicine and pulmonologist at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC). “If we completely eliminate masks and distancing during cold and flu season, we’ll allow all those viruses that have been effectively suppressed to come raging back. There could be a lot of illness.”
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, COPD was the fourth-leading cause of death worldwide and a leading cause of hospital admissions in the United States. The pandemic has led to significant changes in healthcare delivery, including reduced admissions for COPD and other non-COVID illnesses, some of which may have stemmed from patients’ fear of contracting COVID in various hospital settings, as well as a shift toward telemedicine and outpatient COPD management during the pandemic.
To understand what may have occurred to reduce COPD admissions, the researchers compared weekly hospital admissions for COPD in the pre-COVID-19 years of 2018 and 2019, with admissions after the COVID-19 public health measures were instituted. At UMMS, those measures were implemented before April 1, 2020, so the investigators chose the same five-month period in each year for their comparison, April 1 to Sept. 30.
Co-lead author Jennifer Y. So, MD, UMSOM assistant professor of medicine and COPD specialist at UMMC, said electronic medical records from multiple hospitals across a range of communities in the UMMS database facilitated a granular evaluation of changes over time. “We assessed a variety of possible causes that could affect COPD admissions including the presence of multiple diseases or medical conditions and the frequency of COPD exacerbations.”
The database findings were correlated with data on respiratory viral trends from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the period of Jan. 1, 2018, through Oct. 1, 2020.
“We found a 53 percent drop in COPD admissions throughout UMMS during COVID-19. That is substantial, but equally significant, the drop in weekly COPD admissions was 36 percent lower than the declines seen in other serious medical conditions, including congestive heart failure, diabetes and heart attack,” said So.
As more and more people are vaccinated against COVID-19 and many of the public health measures of the past year are relaxed, the researchers warn that a full return to normal may again expose COPD patients to the familiar seasonal triggers.
“Our study did not assess which public health components worked to tame seasonal respiratory viruses, but a simple thing like wearing a mask while riding on public transit or working from home when you’re sick with a cold could go a long way to reduce virus exposure,” said Reed.
So, who is from South Korea, said it is a cultural norm to wear masks during the winter in her native country. “The COVID-19 pandemic has helped a lot of people around the world become more aware of the role of masking and social distancing to reduce the spread of disease,” she said.
Reference: So JY, O’Hara NN, Kenaa B, Williams JG, deBorja CL, Slejko JF, Zafari Z, Sokolow M, Zimand P, Deming M, Marx J, Pollak A, Reed RM. Decline in COPD Admissions During the COVID-19 Pandemic Associated with Lower Burden of Community Respiratory Viral Infections. medRxiv. Posted May 19, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.18.21257383
Source: University of Maryland School of Medicine