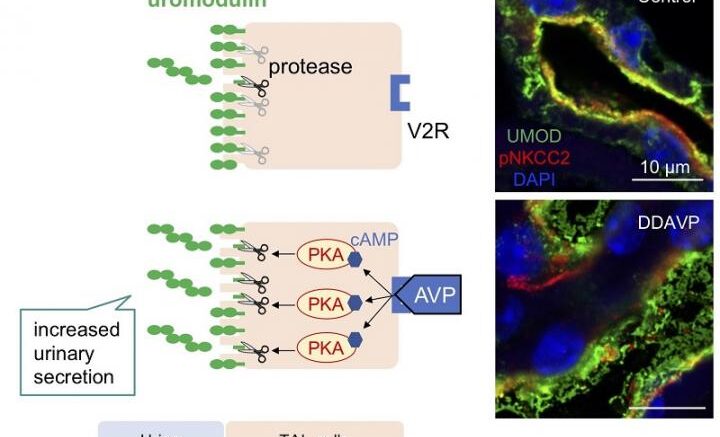
Desmopressin increased short-term urinary secretion of uromodulin and reduced kidney uromodulin abundance in vivo. In vitro studies revealed that this rapid effect depends on cAMP/PKA signaling pathway, cell polarity and probably apical proteases. Courtesy of Department of Nephrology, TMDU
The normal function of uromodulin, a protein that is made in the kidney and secreted into the urine, remains largely unknown. However, higher levels of uromodulin in the urine are related to lower rates of urinary tract infections and kidney stones, while higher levels of this protein in kidney cells are associated with higher rates of hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Researchers from Japan have now uncovered how uromodulin secretion into the urine can be increased by the hormone vasopressin--a finding that may have many practical applications.
In a study published recently in Hypertension, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) revealed that vasopressin receptor stimulation leads to the short-term secretion of uromodulin into the urine in mice. They found that this occurs via the protein kinase A pathway, a common cell signaling pathway that is dependent on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels, in kidney cells.
Most of our knowledge about the role of uromodulin in disease comes from genetic studies. Notably, uromodulin secretion into the urine seems to be particularly important for disease prevention, but little is known about how this secretion might occur. Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) aimed to explore this process in more detail.
"The urinary secretion of uromodulin is associated with protection against many common diseases," says lead author of the study, Azuma Nanamatsu. "We wanted to investigate how to increase this secretion, to develop better therapies in the future."
To do this, the researchers stimulated vasopressin receptors in mice, which has previously been reported to affect uromodulin secretion. When they saw that the treated mice had higher levels of uromodulin in the urine and lower levels in the kidney, they decided to test the effects of increased cAMP on uromodulin secretion in a kidney cell line, because vasopressin receptor stimulation leads to increased cAMP levels.
"We found that uromodulin was secreted from kidney cells when cAMP levels were increased," explains Takayasu Mori, senior author. "This secretion only happened on the apical cell surface, which normally faces the lumen or external space in the kidney."
The authors then found that this secretion of uromodulin could be decreased by treating cells with a protein kinase A inhibitor. Together, their findings suggest that vasopressin/cAMP/protein kinase A signaling is important for the secretion of uromodulin from kidney cells into the urine.
The findings of this study may be used to develop better therapies for diseases that are related to lower urinary uromodulin levels, such as urinary tract infections and kidney stones, as well as for those linked to higher kidney uromodulin levels, such as chronic kidney disease and hypertension.
The article, "Vasopressin induces urinary uromodulin secretion by activating protein kinase A," was published in Hypertension at DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17127
Source: Tokyo Medical and Dental University